QLila Europe's First Live-In-Lab
The Quantitive Live-In-Lab (QLiLa) provides a controlled yet naturalistic environment for studying human behaviour, health and technology interactions. It can generate rich, multimodal datasets to train AI models and test novel healthcare and engineering solutions.
Here are the key engineering and medical areas that QLiLa could be used for:
1. Medical and Health Research Areas
A. Chronic Disease Management
- Diabetes monitoring (continuous glucose monitoring, dietary impacts, lifestyle interventions)
- Cardiovascular health (heart rate variability, blood pressure monitoring, AI-driven early detection)
- Neurological conditions (early detection of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s)
- Respiratory health (sleep apnea, COPD monitoring, air quality impact on breathing)
B. Geriatrics and Healthy Aging
- Fall detection and prevention (AI-driven gait analysis, balance tracking)
- Cognitive health (early dementia screening via passive AI behavior analysis)
- Medication adherence monitoring
C. Mental Health & Cognitive Neuroscience
- Stress and anxiety monitoring (physiological and behavioral biomarkers)
- Sleep disorders (insomnia, circadian rhythm disturbances, polysomnography alternatives)
- AI-driven therapy support (personalized interventions for mental health)
D. Rehabilitation and Physiotherapy
- AI-based movement analysis for stroke recovery or orthopedic rehab
- Wearable and remote physiotherapy solutions
- Digital pain monitoring and management
E. Nutrition and Metabolic Health
- AI-driven dietary intake assessment (smart food tracking, metabolic response analysis)
- Nutritional interventions for obesity and metabolic syndrome
- Gut microbiome and diet interactions
F. Infectious Disease and Public Health
- AI-based symptom tracking (real-time early warning for disease outbreaks)
- Contact tracing and exposure modeling
- Environmental hygiene monitoring
2. Engineering and AI Research Areas
A. Human-AI Interaction and Assistive Technology
- AI-powered personal assistants for health and daily living
- Smart home automation for elderly or disabled individuals
- Voice and gesture-based AI interaction models
B. Wearable and Embedded Sensor Technology
- Smart textiles and biosensors (real-time health monitoring)
- AI-enhanced prosthetics and exoskeletons
- Brain-computer interfaces (BCI) and neurotechnology
C. Robotics and Automation in Healthcare
- Home-based robotic caregivers (AI-driven mobility aids)
- AI-powered rehabilitation robots
- Automated drug dispensing and adherence monitoring
D. Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) & Edge AI
- AI-based edge computing for continuous health monitoring
- Secure, real-time health data processing within smart homes
- Predictive analytics for disease progression
E. Smart Environments and Behavioral Monitoring
- AI-driven behavioral analysis for habit formation and well-being
- Energy-efficient, context-aware smart home adaptation
- AI-driven environmental quality monitoring (air, noise, lighting)
F. Privacy-Preserving AI & Federated Learning in Healthcare
- Decentralized AI models for personalized medicine
- Privacy-centric health data collection and analysis
- Secure federated learning in multi-user environments
3. Validation & Regulatory Testing for AI in Healthcare
- Clinical trial support for AI-based diagnostics and treatments
- Usability studies for AI-powered decision-support systems
- Validation of AI explainability in real-world healthcare settings
This broad spectrum of applications positions QLiLa as a highly interdisciplinary testbed for advancing AI-driven healthcare, behavioural research, and smart assistive technologies.
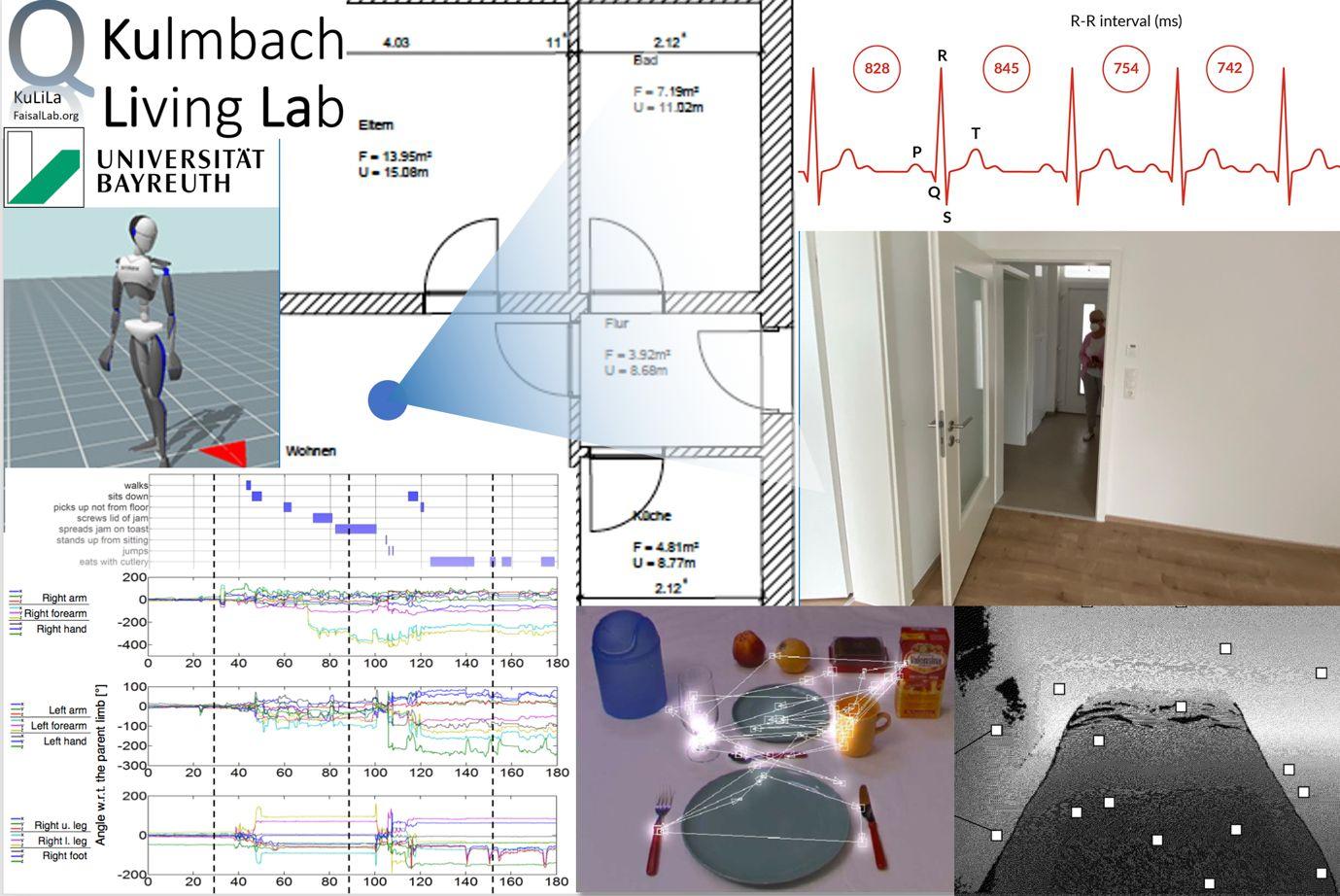
Impressions from Research at the Quantitive Live-In-Lab in Kulmbach - © Prof. Dr. Aldo Faisal
Technical Equipment
Depth Cameras
Smart Clothing Modules
Eye-Tracking Glasses
High-Performance Computers
For more information also see this UBT Press Announcement from January 2023: Smart clothing and artificial intelligence: A new technology for the diagnosis and monitoring of neurological diseases
Join Our Lab
If you want to join our research initiative or partner with us for a project, check out our current Master projects or write us at faisal_lab@uni-bayreuth.de.
Media Highlights
RTL Filming in Kulmbach Live-In-Lab
Wir brauchen Ihr Einverständnis
Um aktuelle Videos, Karten oder Fremdinhalte der UNI Bayreuth einbinden zu können, nutzen wir die Services von Drittanbietern. Diese sammeln unter Umständen Daten zu Ihren Aktivitäten. Unter dem Punkt "Mehr Informationen" finden Sie weitere Details.Publications
B. Kadirvelu et al.: A wearable motion capture suit and machine learning predict disease progression in Friedreich's ataxia. Nature Medicine (2023), DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41591-022-02159-6
V. Ricotti et al.: Wearable full-body motion tracking of activities of daily living predicts disease trajectory in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nature Medicine (2023), DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41591-022-02045-1













